A new fat hormone that controls appetite

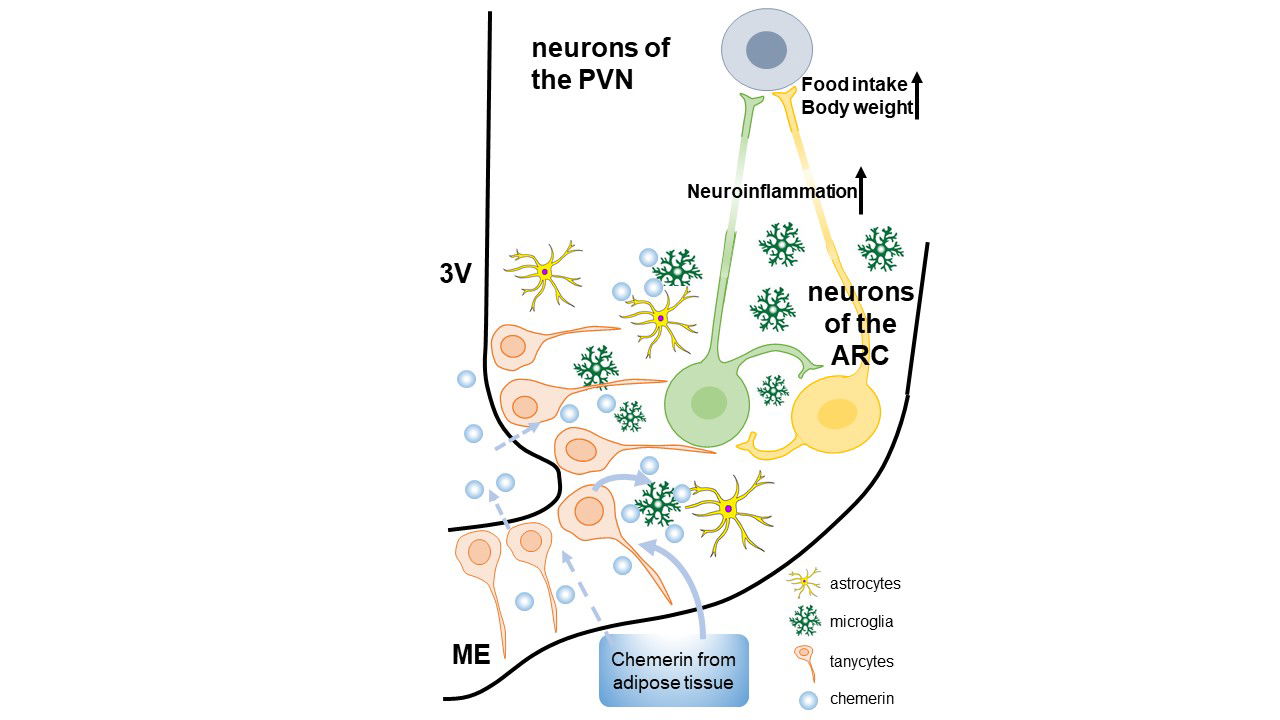
Multiple factors related to modern lifestyle, such as sedentary behaviour and the overconsumption of calorie-dense foods disrupt our body's energy balance and facilitate weight gain. Homeostatic regulation of food intake and energy expenditure results from a complex series of interactions of hormones and neuromodulators in the hypothalamus of the central nervous system to regulate appetite homeostasis. Among the hormones driving this circuitry that link to unwanted effects of modern living is the adipokine chemerin. In this project, we investigate the central role of chemerin in the regulation of appetite, body weight and neuroinflammation. While chemerin is known for its inflammatory role in the immune system, its influence on the brain and neuroendocrine system remains largely unexplored.
References: